Saving power on your computer is important. This ensures your battery life lasts long, saves energy and eventually saves you money in the long run. Windows OS provides a number of options for power saving; including sleep, hibernate and hybrid sleep options.
They are very similar to each other yet there are slight differences between them. In this article we will talk about the difference between sleep and hibernate as well as hybrid sleep.
Sleep vs Hibernate vs Hybrid Sleep
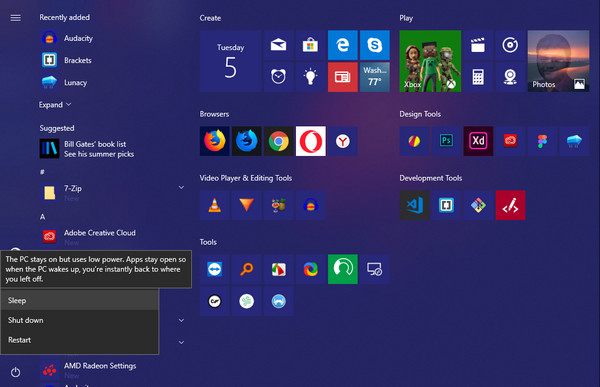
Sleep
Putting your computer in this state enables you to put it in power-saving mode and go back exactly where you left off anytime you wish. It simply puts the computer into low power state without closing the current commands. It is like pausing a video. You can go away, come back later and pick up where you left. All the open documents, files or applications are committed to internal memory (RAM) before the computer goes to ‘sleep.’ Resuming your activity takes only seconds. You can use sleep mode to save power on your device while not working on it, without the inconvenience of closing your work.
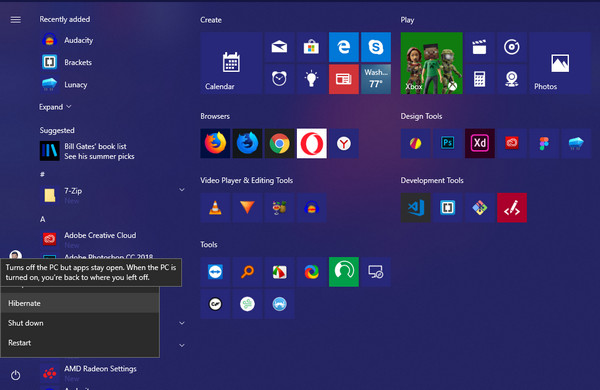
Hibernate
This option is almost the same as sleep mode. It is basically designed for laptops since they have limited battery power availability. The word hibernate means primarily ‘suspend to disk.’ When you choose to set your laptop to hibernation, it moves all your open apps and folders to the hard disk. This means it can fully shut off, using no power. This is unlike sleep mode, where the computer is still on but uses low power. Therefore, you can maintain power on your laptop optimally. Hibernation is best used when you do not plan on using your laptop for a long time, and you have no immediate power source. When you reopen the laptop, the apps, files or documents will be open, and you can resume from where you left off.
Hybrid Sleep
This mode combines both the sleep and hibernate power-saving features. It is designed for desktop computers. When activated, it sends the open files both to the memory and the hard disk. It then goes into low-power mode. When the memory cannot be accessed, like in the case of power failure, the open files are obtained from the hard disk. This dual backup system ensures reliability. Also, when your computer is in this mode, any command for ‘sleep’ automatically changes to hybrid sleep.
These three power-saving options are a great way to conserve your battery while you do not need the computer/laptop. The options are found on the Power option in the Windows Start menu or Settings. Depending on your frequency in using your Windows, you can choose any of the options to effectively save your power.






Leave a Comment